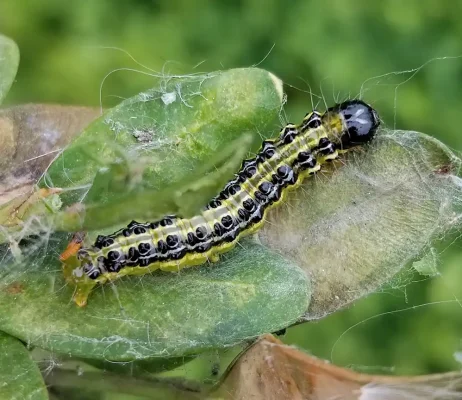
Plant Your Trees Like a Pro: Tips from the Experts at Beautiful Trees
Discover professional tree planting tips from certified arborists Jen Llewellyn and Johl Anderson on the Beautiful Trees podcast. Get step-by-step guidance for planting trees that thrive in Ontario’s landscape.